News
Sidebar
Categories
Constant CO2 Level in Greenhouse
Controlled CO2 gas inflow and improved air mixture can help maintain optimum CO2 levels in small indoor greenhouses or grow rooms. These were the lessons learned after working with a client who was attempting to control the CO2 levels in a group of 3 10x20” greenhouses.
The client wanted to maintain different consistent CO2 levels in each greenhouse to test the effects on the plants inside. To control the CO2, he used our iSense 1% CO2 Level Controller, a more industrial version of our Day Night CO2 Monitor & Controller for Greenhouses.
In one test greenhouse, the CO2 controller was set to turn on a CO2 Tank Regulator with Solenoid Valve at 700ppm and turn it off at 1,400ppm. While the controller correctly turned the regulator on at 700ppm, the CO2 levels were overshooting 1,400ppm before switching off the solenoid on the regulator. As a result, the clients was seeing wild swings of CO2 levels instead of the consistent level required for his experimentation.
After looking at his CO2 levels vs. time graphs, we noticed a pattern of a quick rise in the level of CO2, followed by slow drops. This lead to the conclusion that the greenhouse was being quickly flooded with CO2 before the CO2 sensor in the controller had a chance to react to the change in CO2 levels.
In other words, the problem was being caused by inefficient air mixture in an enclosed area.
In a perfect world the CO2 flow rate could be set to exactly match the CO2 loss. However, in the real world, minimum and maximum level switches are required to turn the regulator on and off to keep the CO2 levels within a specified range.
We suggested three changes to the client’s setup to help solve his problem.
- Increase air circulation with fans, especially ones placed near the CO2 gas inlet into the greenhouse.
- Make a CO2 delivery tube like industrial greenhouses with propane CO2 systems use. Drill small holes in a long piece of flexible tubing that runs the length of the greenhouse, then hang the tubing above the plants. Since carbon dioxide is heavier than normal air, it will naturally mix as it falls.
- This decreases the amount of CO2 released between the time the room reaches the optimum CO2 level and the controller senses it. In addition, a good regulator with flow control not only limits the amount of CO2 that is released, but it maintains a consistent level of flow as the CO2 is used and the tank pressure changes.
Using our suggestions, the client will be able to maintain a more consistent CO2 level in the test greenhouses in order to complete their experiments.
Compost & Soil Gas Testing: 3 Inexpensive Solutions
Most of us who live in the city think of soil as “dirt.” However, soil is actually a living environment of underground plants, animals, and microorganisms that, like humans, need food, water and oxygen to survive.
Soil gas testing is the process of measuring oxygen, carbon dioxide, methane, radon, and other gases in soil. For example, large-scale composters monitor the gases inside long, narrow piles of plant material and manure called wind-rows. The right combination of moisture, temperature, oxygen and CO2 is required to feed the aerobic microbes that turn the materials into compost. Alternatively, biologists measure CO2 or methane gassing from fields or wetlands for long term environmental studies.
To measure compost or soil gas testing, here are 3 inexpensive solutions. Each of them rely on the fact that soil is porous, and over time the gas inside the tube will match the atmosphere in the soil.
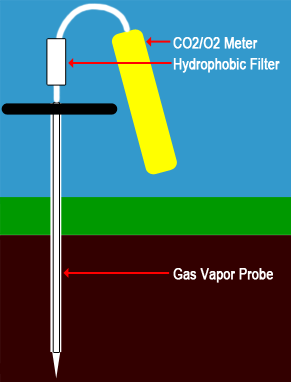 Gas Vapor Probe
Gas Vapor Probe
A Gas Vapor Probe provides the most scientific method for measuring soil gases. While you can purchase $2,500-$4,500 professional kits with an electric bore-hole drill that will reach virtually any depth, this $350 hand-held probe from AMS provides an inexpensive solution for shallow soil or compost pile testing. Either of these probes will work with our CO2+CH4 Sampling Data Logger or our CO2 Sampling Data Logger for soil gas testing. the built-in sampling pump will evacuate the tubing after a few seconds, and you can get an accurate measurement of the soil gas levels at the probe tip.
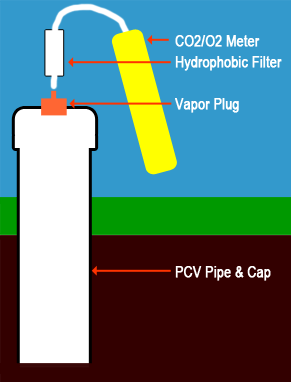 Permanent Sampling Holes
Permanent Sampling Holes
For clients who need to monitor several soil gas stations over time, an inexpensive solution is to build your own monitoring station with PVC pipe. This station can be built for about $40 in parts. After the sampling hole is dug to the desired depth, a capped PVC pipe with a Locking Vapor Extraction Plug mounted to the top provides a low-cost, permanent station. With the vapor plug, you will not contaminate the gas inside the pipe with outdoor air. When you are ready to take a sample, attach the tubing, open the air lock, and take a reading with any of our hand-held sampling meters.
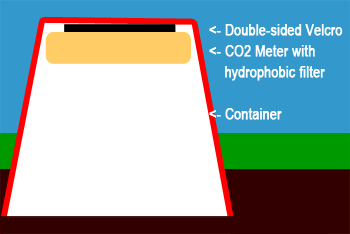 Shallow Sampling Container
Shallow Sampling Container
For long-term data logging in shallow soil, you can use a 1% CO2 Data Logger mounted under a leak-proof container. Dig a hole to the desired depth, mount the data logger inside the container using double-sided Velcro, and bury the container in the hole securely. The 1% CO2 Data Logger with 6,000mAh Li-Ion batteries and the optional hydrophobic filter kit can record CO2, temperature and %RH levels for up to 6 months on a single charge.
Stay Informed with Our Latest Updates
Subscribe to our newsletter for the latest news, product updates, and industry insights.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.
Still need Help? Talk to an Expert.
We'll be happy to help you find the right product!
Call us at 877.678.4259.



 Gas Vapor Probe
Gas Vapor Probe Permanent Sampling Holes
Permanent Sampling Holes Shallow Sampling Container
Shallow Sampling Container